What Is Spam Email & Why Your Emails Go to Spam (How to Stop It)


Email spam is one of the most significant challenges faced by businesses, marketers, and product teams that rely heavily on email. Even legitimate emails often fail to reach the inbox and instead land in spam or junk folders, resulting in low open rates, lost conversions, and damaged sender reputation. If you’ve ever wondered, “Why does my email go to spam even when it’s legitimate?” the answer usually lies in sender reputation, list quality, and technical signals that spam filters evaluate automatically.
The reality is simple: most spam issues are not caused by bad content, but by technical signals, list quality problems, and sender trust issues that spam filters detect automatically.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
Spam email is any unwanted or untrusted message that email providers filter out to protect users. These emails often show signs of poor sender reputation, misleading content, or unsafe sending practices. Even legitimate emails can be marked as spam if they trigger these risk signals.
Spam email commonly includes:
Email providers do not judge intent. They judge behavior.
Spam classification is behavior-based, not intent-based. Well-meaning senders are frequently flagged when their email practices resemble spam behavior, such as:
| Legitimate Email | Spam Email |
|---|---|
| Sent with user consent | Sent without permission |
| Relevant and expected | Irrelevant or deceptive |
| Clear sender identity | Fake or misleading sender |
| Personalized content | Generic mass messaging |
| Easy unsubscribe option | No unsubscribe or hidden links |
| Proper authentication | Missing or forged authentication |
Spam filters don’t punish businesses. They protect users.
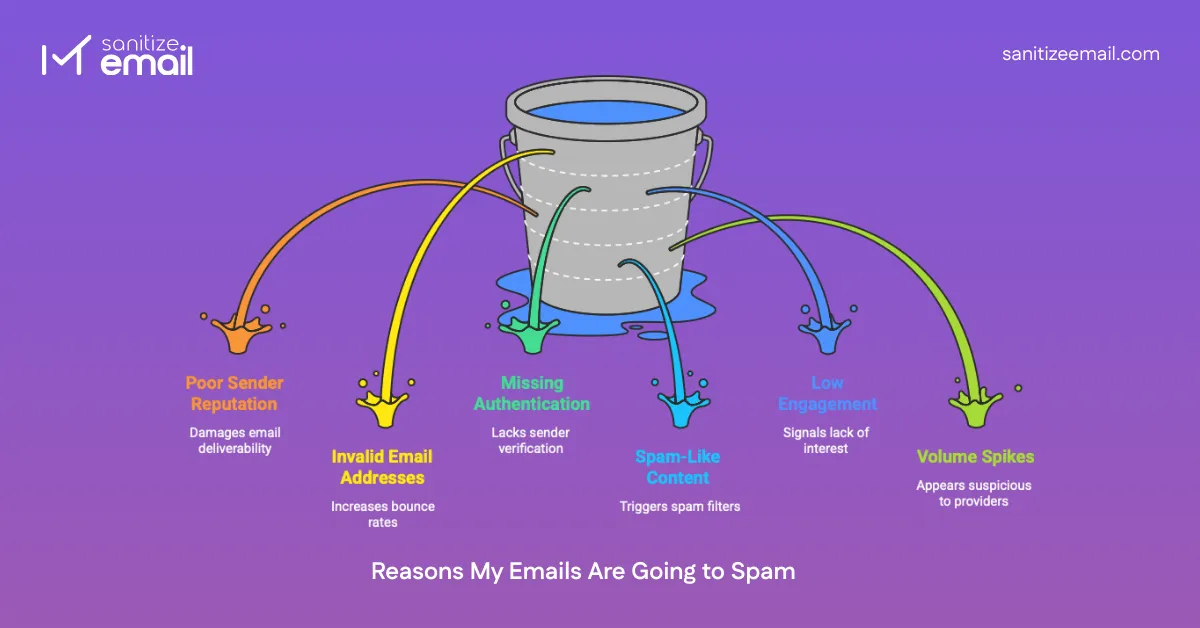
Emails may be directed to spam due to issues with sender reputation, list quality, authentication failures, engagement signals, and sending behavior. For businesses, emails going to spam often indicate deeper issues with list hygiene, authentication, or inconsistent sending patterns rather than content alone. These are the most common reasons for email spam identified by modern spam filters.
So, what makes an email go to spam is rarely a single mistake, but a combination of trust, behavior, and technical signals evaluated over time.
Your sender reputation is like a credit score for email. Domains and IPs build trust based on historical behavior. High spam complaints, elevated bounce rates, blacklist appearances, and inconsistent sending patterns all reduce trust.
Sending emails to invalid or inactive addresses quickly damages reputation and causes future emails to be filtered automatically. This is especially critical for SaaS platforms offering free trials, where fake or disposable signups can quietly erode sender trust. If you're evaluating tools to prevent this at the source, see our breakdown of the best email verification tools for SaaS.
Email lists naturally decay. People change jobs, abandon inboxes, or stop engaging. Sending to these addresses causes hard bounces and signals poor list hygiene. This is why maintaining proper email hygiene, including cleaning your email list regularly, is critical for long-term deliverability.
Even 2–3% invalid addresses can significantly harm deliverability over time.
Without proper authentication, email providers cannot verify that your emails are legitimate. Unauthenticated emails appear suspicious and are frequently filtered.
Authentication is no longer optional. It is a baseline requirement for inbox delivery.
Certain content patterns increase spam risk:
While content alone rarely causes spam placement, it can amplify existing trust issues.
Spam filters track how recipients interact with your emails. Low opens, deletes without reading, and a lack of replies indicate that the content is unwanted.
Consistently low engagement trains filters to deprioritize your messages.
Abrupt increases in sending volume look suspicious, especially from new or inactive domains. Consistent, predictable sending builds trust. Erratic behavior destroys it.
Spam filters are automated systems used by email providers to decide whether an email should land in the inbox, spam folder, or be blocked entirely.
Modern filters analyze hundreds of signals, including:
Major providers like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo use machine learning systems trained on billions of emails to make real-time decisions.
Spam filtering is probabilistic, not absolute. The goal is risk reduction.
Spam filters evaluate every email using a combination of sender trust, recipient behavior, and technical signals. In simple terms, they look for:
If multiple risk signals appear together, the email is automatically routed to spam or junk folders.
One of the most overlooked causes of spam issues is poor email list quality. Poor list quality is almost always the result of neglected email list hygiene over time. Many senders focus on content and authentication while ignoring the foundation: who they are emailing.
Email list cleaning is the process of removing problematic addresses, including:
A dirty list:
A clean list:
Rule of deliverability: List quality matters more than list size.
If you do only one thing to improve deliverability, clean your email list.
Email list cleaning tools like SanitizeEmail and other email verification tools help remove invalid, disposable, and risky addresses before sending, directly reducing bounce rates and spam complaints.
For a detailed breakdown by use case, see our complete guide on how often to clean your email list.
Email authentication is the technical foundation of email deliverability. It helps email providers verify that your emails are truly sent by you and not forged by scammers or spammers.
As of 2024-2025, Gmail and Yahoo enforce strict authentication requirements for bulk senders. Without proper setup, your emails will be rejected or automatically sent to spam.
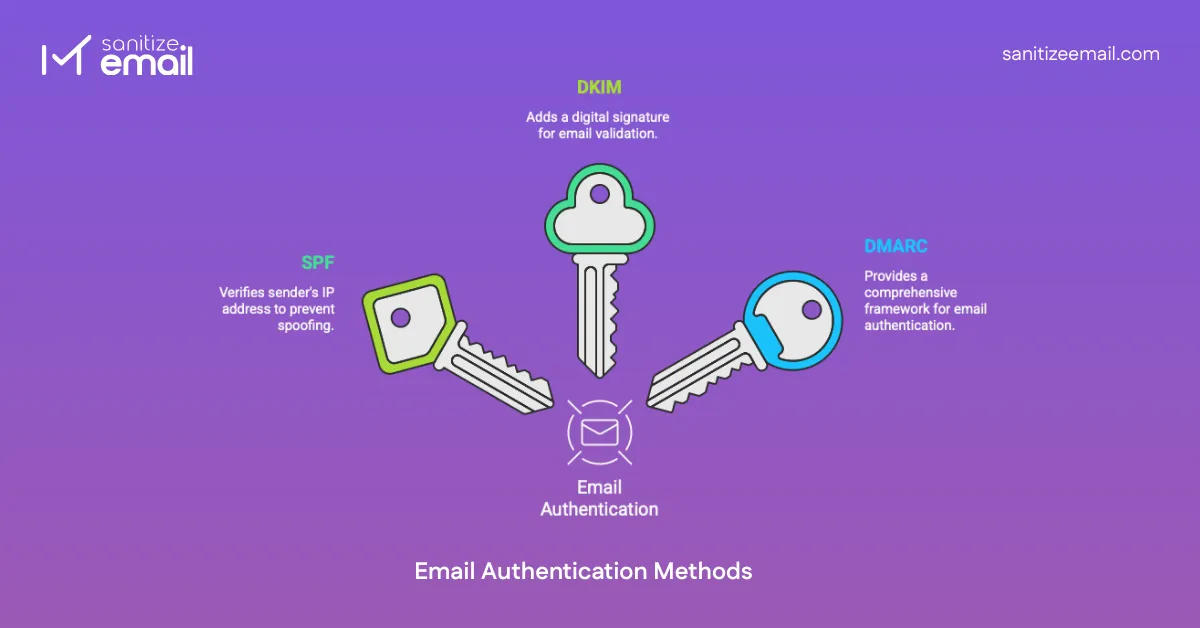
Three main authentication methods work together:
SPF specifies which mail servers and IP addresses are authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain.
How it works: You publish a TXT record in your domain's DNS settings that lists all legitimate sending sources. When an email arrives, the receiving server checks this record to verify the sender is authorized.
Without SPF:
DKIM adds a digital signature to your emails to ensure the content hasn't been tampered with during transit.
How it works: Your mail server adds an encrypted signature to the email header. The receiving server uses your public key (published in DNS) to verify the signature matches the content.
What DKIM prevents:
DMARC is a policy layer that sits on top of SPF and DKIM. It tells email providers exactly what to do with emails that fail authentication checks.
DMARC policy options:
Why DMARC matters:
Starting in 2024 and continuing into 2026, major email providers require:
✅ Valid SPF record
✅ Valid DKIM signature
✅ DMARC policy published
✅ SPF and DKIM alignment
✅ One-click unsubscribe for bulk senders
✅ Spam complaint rate below 0.3%

If your emails are landing in spam, here’s how to fix it.
What to do: Remove invalid, inactive, and risky email addresses using an email validation tool.
How to do it:
a. Export your complete email list from your ESP (Email Service Provider)
b. Upload the list to an email validator
c. Review the validation results:
d. Import the cleaned list back to your ESP
e. Set up automated validation for ongoing list hygiene
Not sure which tool to use? Check out our guide to the best email verification tools in 2026 to find the right solution for your needs.
What to do: Properly configure all three authentication protocols to prove you're a legitimate sender.
How to set up SPF:
How to set up DKIM:
How to set up DMARC:
What to do: Ensure your mail server is correctly configured and not triggering technical red flags.
Misconfigured mail servers can cause immediate delivery failures, even if your content is perfect. Common issues include:
How to test:
What to do: Craft professional, valuable emails that avoid spam triggers and provide genuine value.
Content best practices:
What to do: Maintain a steady, predictable sending schedule to build trust with email providers.
Why consistency matters: Email providers track sending patterns. Erratic behavior triggers suspicion:
❌ Bad: Send 50K emails once a month ✅ Good: Send 12K emails weekly
❌ Bad: No emails for 3 months, then large campaign ✅ Good: Regular weekly or bi-weekly sends
❌ Bad: Volume varies wildly (5K, then 50K, then 2K) ✅ Good: Predictable volume with gradual increases
Best practices:
What to do: Track key email metrics to identify and address deliverability problems early.
Bounce rate
Spam complaint rate
Open rate
Unsubscribe rate
Engagement rate
Inbox placement rate
Outlook and Yahoo use the term “junk mail” instead of “spam,” but the filtering logic is largely the same.
Small trust signals matter.
An email spam checker is a diagnostic tool that analyzes your email setup, content, and configuration to identify potential spam risks before you send emails to your list.
These tools are essential for proactive deliverability management. Rather than discovering problems after poor campaign performance, spam checkers help you catch and fix issues in advance.
Checks if your domain or IP appears on major email blacklists such as:
Why it matters: Blacklist appearance can block delivery to thousands of recipients instantly.
Verifies proper configuration of:
Why it matters: Missing or misconfigured authentication is a top reason for spam folder
placement.
Analyzes email content for:
Why it matters: Content triggers can override a good technical setup.
Evaluates:
Why it matters: Reputation is the single biggest factor in deliverability.
Checks for:
Why it matters: Technical misconfigurations cause immediate delivery failures.
Deliverability isn't a one-time fix — it's an ongoing process that requires consistent attention and good practices.
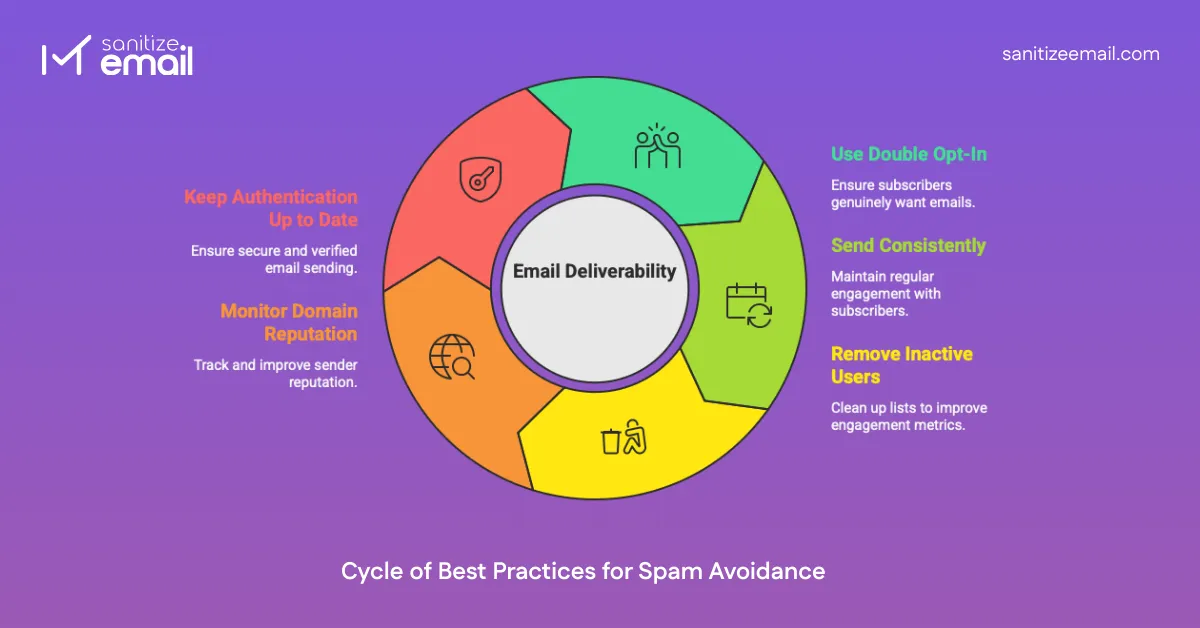
What it is: New subscribers must confirm their email address before receiving emails.
How to implement:
Long-term benefits:
Why consistency matters: Email providers reward predictable behavior and penalize erratic sending.
Consistency guidelines:
Results:
Removal process:
Why removal helps:
Industry insight: A list of 10,000 engaged subscribers always outperforms 100,000 inactive contacts.
What to monitor:
Tools for monitoring:
Action triggers:
Regular authentication maintenance:
Quarterly:
When making changes:
Common mistakes:
❌ SPF includes too many lookups (limit: 10)
❌ Old sending sources still in SPF
❌ DKIM keys rotated, but DNS not updated
❌ DMARC set to "none" indefinitely
❌ Not monitoring DMARC reports
Spam filters exist to protect users, not to punish legitimate senders. Understanding this mindset shift is crucial — if you approach email from your recipients' perspective, most deliverability problems solve themselves.
The vast majority of spam issues are caused by fixable problems:
None of these problems is permanent. With the right approach and tools, any sender can achieve consistent inbox placement.
Avoiding spam requires more than fixing content. It depends on using the right tools at each stage of the email marketing workflow, which we explain in our must-have email marketing tools guide.
✅ Verify your email authentication with a free DMARC checker
✅ Test your email server configuration with an SMTP tester
✅ Clean your contact list using a free email validator
✅ Check inbox placement with an email delivery test
These checks help you identify and fix deliverability issues before they affect your campaigns.